Netnod’s IXP Architecture
Technical overview
Netnod’s Internet exchange points are built on Ethernet technology. They are a layer 2 service with no routing facilities existing within the exchange points.
For customers connecting to Netnod at a data centre, one cross connect is needed per port. If you order a redundant connection in Stockholm, Copenhagen or Helsinki (see below), you will need two cross connects. In that case, you will be guaranteed diverse paths to ensure redundancy.
Redundant ports vs single port
At the Netnod IXes in Stockholm, Copenhagen and Helsinki, the IX has two redundant peering fabrics located in separate, secure sites. There are also a number of co-location sites with switches and DWDM equipment to backhaul traffic to the two main sites. The switch fabrics in these metros use a dedicated fibre path for each switch to ensure multiple, redundant paths.
Customers at the IXes in Stockholm, Copenhagen and Helsinki can buy a redundant connection which gives them two ports connected to the separate switch fabrics on the Internet Exchange. These switch fabrics are labelled “Green” and “Blue”.
As you can see below, Network A has redundant ports and connects to the Blue peering fabric with one port and to the Green peering fabric with a second port. Networks B and C use a single connection over a single port to connect to the Blue AND Green peering LANs.
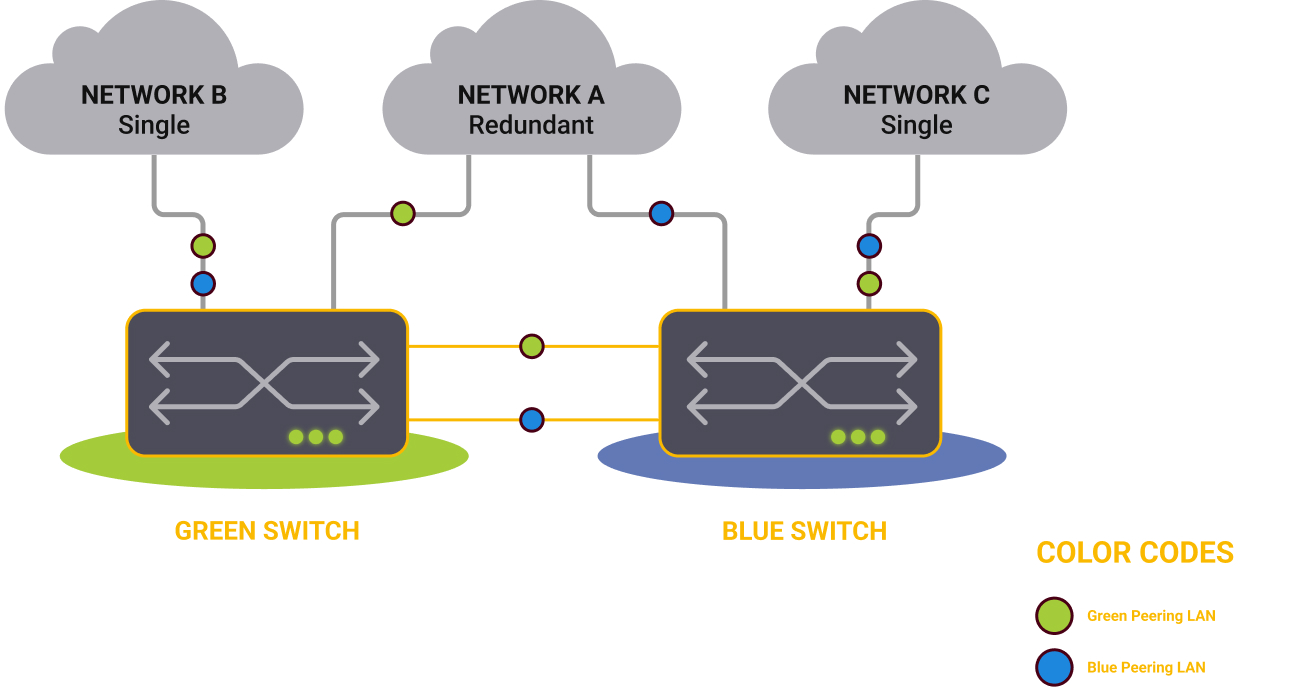
The Netnod IXes in Gothenburg, Sundsvall, and Luleå do not currently have physical redundancy as an option. However, if there is customer demand, Netnod will add redundant switches to any of our IXes.
MAC addresses
The ports on the peering LAN will be configured to allow only the connected customers' interface-MAC-addresses. The MAC addresses of the customer's interfaces need to be provided to Netnod in advance. In case of a change in the customer's hardware, Netnod needs to be notified at least one full working day in advance.
IP addresses
All Netnod IXes support IPv4 and IPv6. Each VLAN connection should always have one of each.
The amount of IP addresses needed for each customer depends on two things: if the exchange is redundant and the MTU/VLAN setup on the peering LAN.
Netnod will assign and distribute IP addresses to the connected customers.
MTU/VLAN setup
Currently there are 2 standard setups:
Type:
-
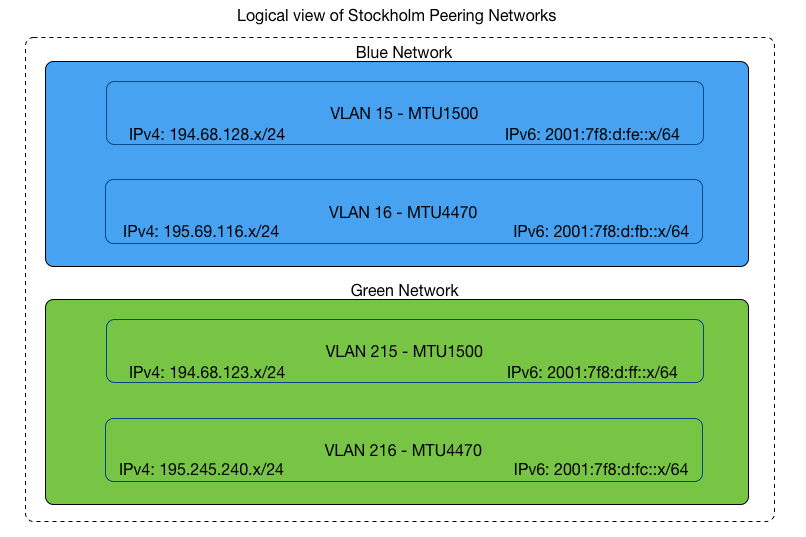
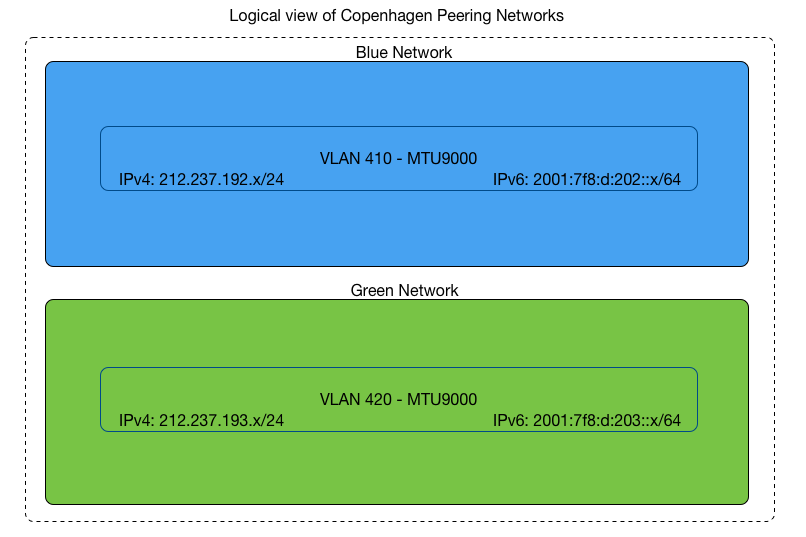
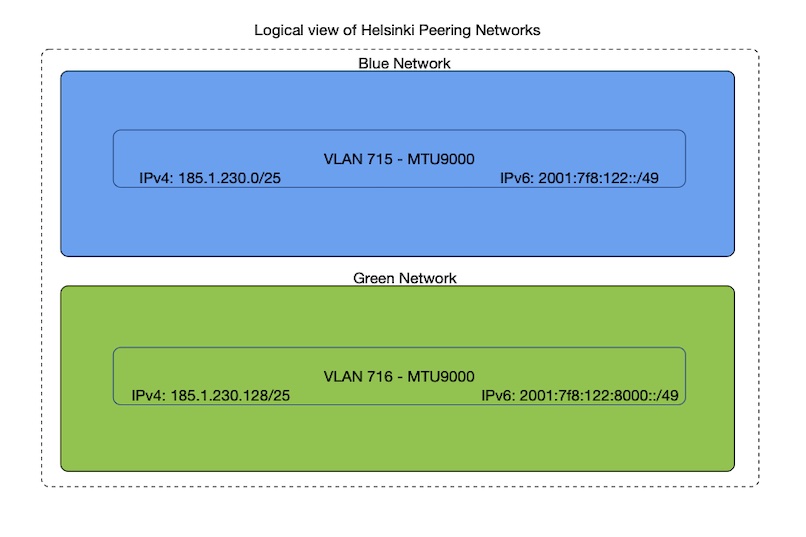
MTU 9000 only peering VLAN per peering LAN (1 IPv4 + 1 IPv6)
-
MTU 1500 + MTU 4470 peering VLANs per peering LAN ( 2 IPv4 + 2 IPv6)
If the exchange is Redundant each peering LAN is configured with either 1 or 2 VLANs per peering LAN according to the two types shown above.
The VLANs are implemented according to IEEE802.1Q. As there is no connection within the exchange points between the different VLANs, a customer that communicates with parties using different MTU-sizes needs to have a connection to each VLAN they want to exchange traffic on.
Summary of MTU/VLAN setup at Netnod IXes
| Exchange Location | Available VLANs | MTU-size(s) | Redundancy possible |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stockholm | BLUE GREEN |
1500+4470 1500+4470 |
Yes |
| Copenhagen | BLUE GREEN |
9000 9000 |
Yes |
| Helsinki | BLUE GREEN |
9000 9000 |
Yes* |
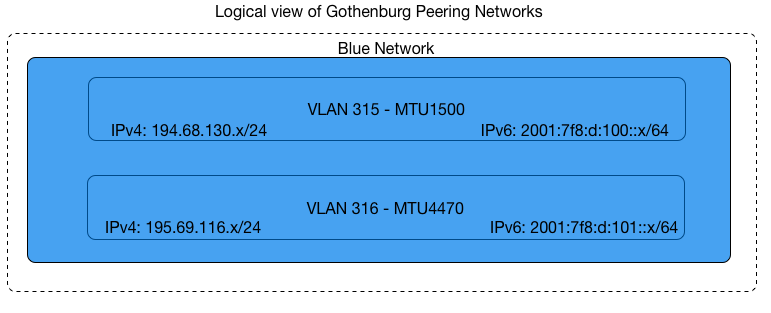
| Gothenburg | BLUE | 1500+4470 |
No |
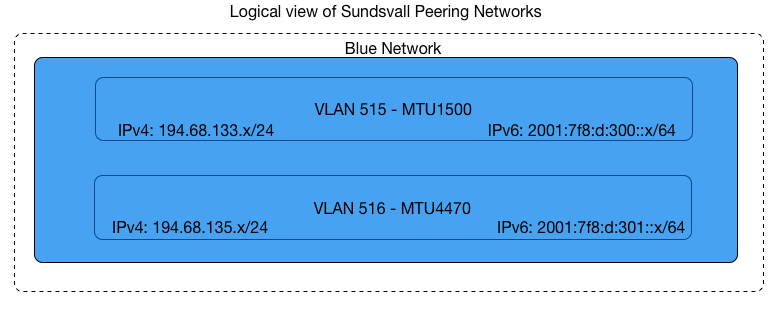
| Sundsvall | BLUE | 1500+4470 |
No |
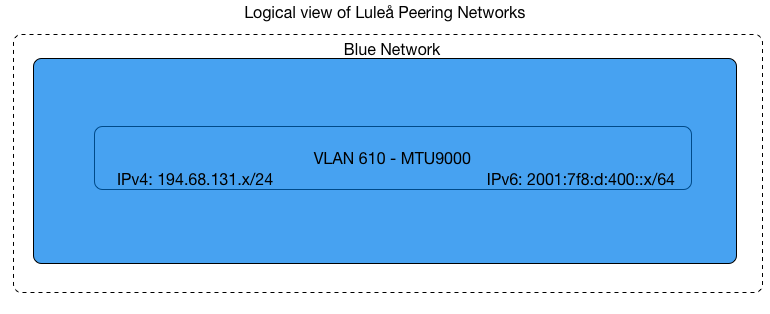
| Luleå | BLUE | 1500+4470 |
No |
*Customers who need local redundancy in Helsinki are advised to connect to HE7
Setup in Stockholm:
Setup in Copenhagen:
Setup in Helsinki:
Setup in Gothenburg:
Setup in Sundsvall:
Setup in Luleå:
Unicast traffic
Peering between a customer’s routers through the exchange point will be done via BGP4. Any kind of tunneling is explicitly forbidden.
Multicast traffic
Multicast traffic is supported over the exchange points.
